Optimal Agricultural Land Use: An Efficient Neutrosophic Linear Programming Method
Main Article Content
Abstract
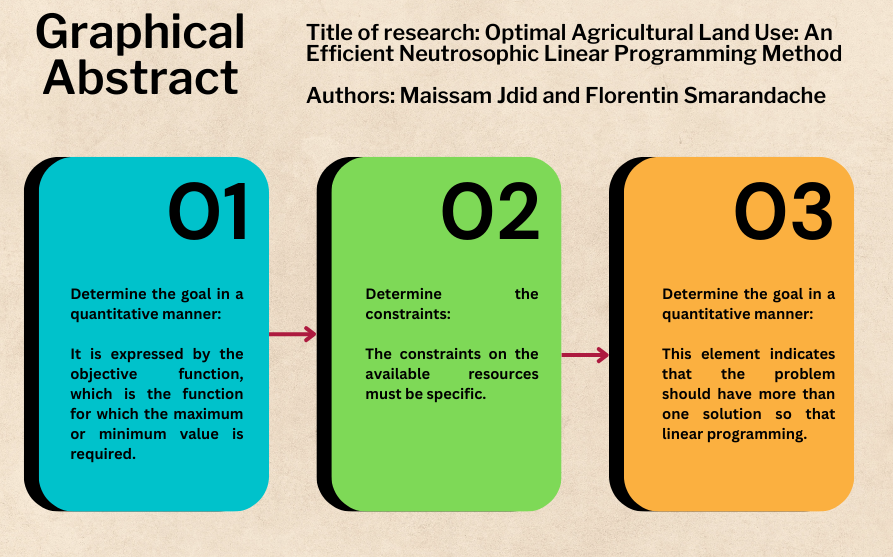
The increase in the size of the problems facing humans, their overlap, the division of labor, the multiplicity of departments, as well as the diversity of products and commodities, led to the complexity of business and the emergence of many administrative and production problems. It was necessary to search for appropriate methods to confront these problems. The science of operations research, with its diverse methods, provided the optimal solutions. It addresses many problems and helps in making scientific and thoughtful decisions to carry out the work in the best way within the available capabilities. Operations research is one of the modern applied sciences that uses the scientific method as a basis and method in research and study, and its basic essence is to build a model that helps management in making decisions related to difficult administrative problems. For example, the military field, financial aspects, industry, in construction for building bridges and huge projects to evaluate the time taken for each project and reduce this time, financial markets and stocks and forecasting economic conditions, in hospital management and controlling the process of nutrition and medicines within the available capabilities, in agriculture Agricultural marketing and many other problems that have been addressed using classical operations research methods. We know that the agricultural sector is one of the important sectors in every country, and the agricultural production process is regulated by those responsible for securing the needs of citizens. Also, those responsible for the agricultural sector are responsible for rationalizing the agricultural process so that the surplus is saved. Due to the difficult circumstances that the country may be going through, in this research, we will reformulate the general model for the optimal distribution of agricultural lands using the concepts of neutrosophic science.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.