Revolutionizing Early Detection: The Influence of Machine Learning in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Diagnosis
Main Article Content
Abstract
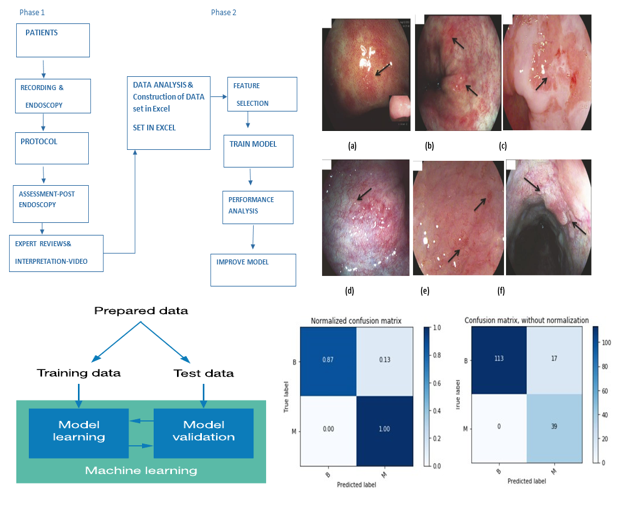
Machine learning is an analysis technique of big data that uses computers and mathematical models to develop algorithms. These algorithms are applied in many situations and one of the most common uses is in developing prediction models. Machine learning is the activity of making prognosis of other data points which are related to the self using key factors from a dataset. It is designed to effectively predict the dysplasia within a given setting using machine learning algorithms on a dataset with primary focus on Barrett’s Esophagus. The study investigates the use of five classification methods: As per the classification, the techniques identified include Naïve Bayes, Support Vector Machine (SVM), Decision Tree, K-Nearest Neighbors, and Logistic Regression. Barrett’s Esophagus Below are the methods applied using and without Principal Component Analysis (PCA) on the special dataset of Barrett’s esophagus. The primary objective is the identification of the effectiveness of each algorithm by comparing their functional characteristics such as F1 score, recall value, accuracy percentage, precision ratio, and specificity coefficient. From the results obtained from the experiments, two algorithms that yield good accuracy for predicting Barrett’s esophagus in this dataset are the SVM algorithm with PCA and Logistic Regression algorithm with PCA and both algorithms returned review ratings of 1. undefined This career has earned a maximum Score of 0.1000, Naïve Bayes perform well in the assessment with 0.964 of accuracy, it followed by K-Nearest Neighbors with 0.9349 and Logistic Regression with 0.923.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.