Neutrosophic Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Framework for Sustainable Evaluation of Power Production Systems in Renewable Energy Sources
Main Article Content
Abstract
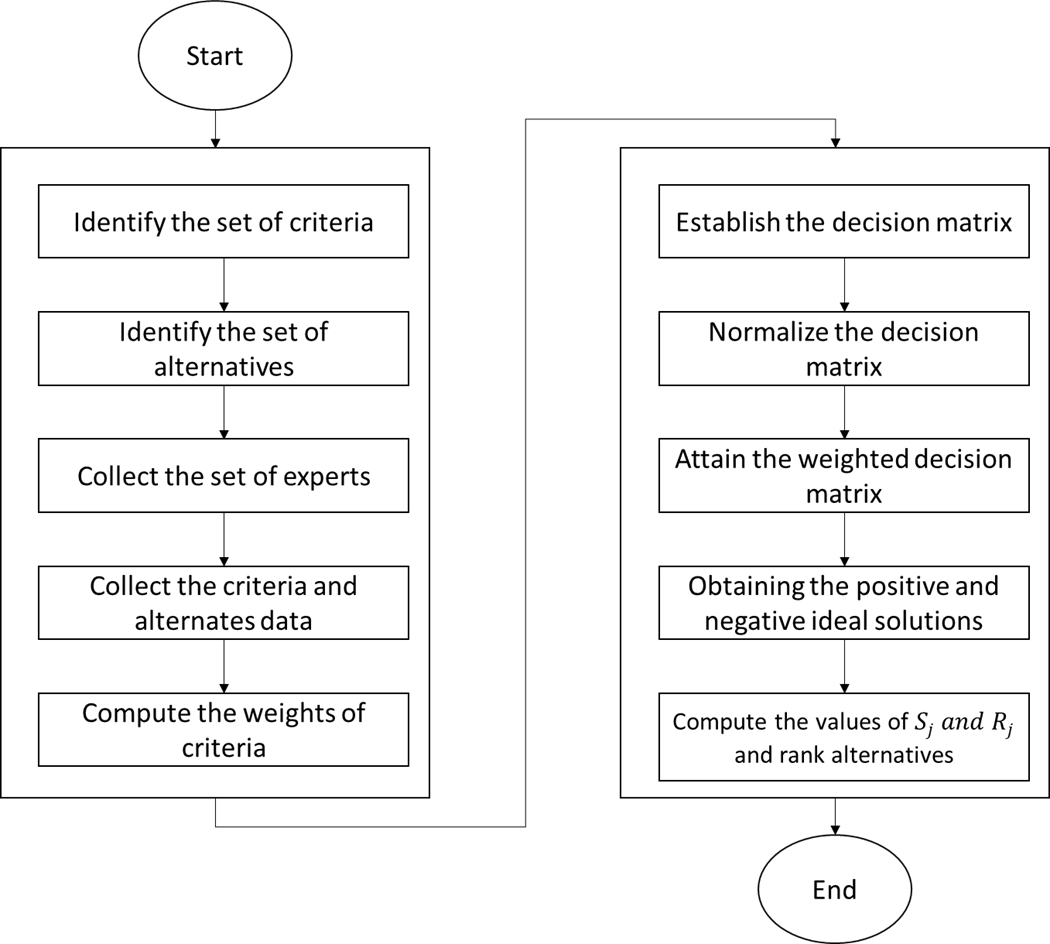
To make the change to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future, it is essential that power production systems be evaluated sustainably. To estimate the overall sustainability performance of various power production systems, this evaluation takes into account a wide range of parameters. Impact on the environment, availability of renewable resources, resource efficiency, social and economic implications, economic feasibility, grid integration and dependability, technical maturity, and scalability are all taken into account. Stakeholders may make better judgments and give higher priority to power production systems that take into account environmental impacts, resource efficiency, social impacts, and economic viability by evaluating these factors. So, we used the multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) approach VIKOR to assess the power production systems in the sustainability criteria. The VIKOR method is used to rank the several alternatives. We integrated the neutrosophic set with the VIKOR method to deal with inconsistent information. We used seven criteria and ten alternatives in this study. The development of a sustainable and resilient energy sector is aided by the sustainable evaluation of power production systems, which in turn helps to reduce the effects of climate change and safeguard the environment.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.